Introduction
Von Willebrand factor [VWF] is a multimeric glycoprotein ranging in size from small to ultra-large molecular weight forms of up to 20 x 106 Daltons [Da]. It is synthesised in:
1. The vascular endothelial cells where it is stored in the Weibel-Palade bodies prior to release.
2. The bone marrow megakaryocyte and so is present in platelets.
VWF is synthesised as a series of ultra-large multimers that are degraded by the metalloprotease ADAMTS13 (A Disintegrin-like And Metalloprotease domain with Thrombospondin type I motifs). A deficiency of ADAMTS13 leads to the accumulation of ultra high molecular weight VWF multimers and the clinical and laboratory features of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP). Assays for ADAMTS13 are covered elsewhere.
VWF has two primary roles:
- As a carrier protein for Factor VIII preventing its proteolytic degradation in plasma
- As an adhesive protein involved in the interaction between platelets and the blood vessel wall. Endothelial cell damage exposes sub-endothelial collagen which binds to VWF triggering a conformational change in the molecule facilitating binding to the platelet GpIb-V-IX complex.
The gene for VWF spans approximately 172kb of genomic sequence, consists of 52 exons, maps to chromosome 12 [12p13.3] and encodes a protein of 2813 amino acids that includes a signal peptide of 22 amino acids, a pre-propeptide of 741 amino acids [residues 23-763] and a mature protein of 2050 amino acids [residues 764-2800]. The mature protein is divided into a series of domains that contain the various functional domains - see Reference 1. The mature VWF protein found in the plasma has a half-life of approximately 12 hours (range 9–15 hours).
An unprocessed partial VWF pseudogene [exons 23-34] exists on chromosome 22.
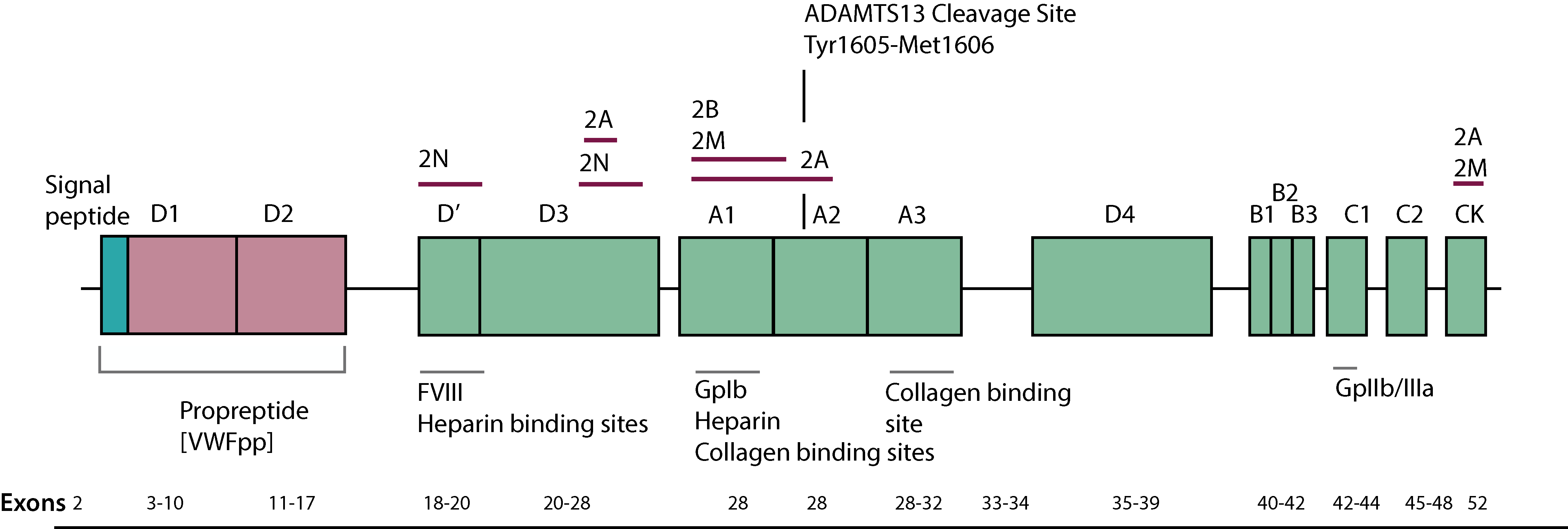
Click HERE to view an expanded view of the above image.
Von Willebrand Factor: Summary of Abbreviations
| Designation | Summary |
|---|---|
| von Willebrand Disease [VWD] | The disorder due to a deficiency or functional abnormality of von Willebrand Factor |
| von Willebrand Factor [VWF] | Multimeric glycoprotein that acts both as a carrier protein for FVIII and as an adhesive protein in the platelet-vessel wall interactions |
| von Willebrand Factor Ristocetin Cofactor Activity [VWF:RCo] | A functional assay of plasma VWF based upon the degree of platelet agglutination induced after the addition of Ristocetin |
| VWF:GPIbR | Assays that are based upon Ristocetin-induced binding of VWF to a recombinant wild-type [WT] GPIb fragment. |
| VWF:GPIbM | Assays that are based upon spontaneous binding of VWF to a gain-of-function variant GPIb fragment |
| VWF:GPIBA | An assay that measures the ability of VWF to bind to GPIbα |
| von Willebrand Collagen Binding Activity [VWF:CB] | A functional assay of VWF that quantifies the ability of VWF to bind to collagen |
| VWF:Ab | Assays that are based upon the binding of a monoclonal antibody to the GPIbα VWF binding site in VWF located in the A1 domain |
| Von Willebrand Activity [VWF:Act] | A functional assay of plasma VWF that uses a monoclonal antibody that targets the part of the VWF molecule that binds to the GpIb receptor. |
| von Willebrand Factor Antigen [VWF:Ag] | An immunological assay that quantifies the amount rather than the function of VWF in plasma |
| von Willebrand Factor Propeptide [VWFpp] | The propeptide of von Willebrand Factor |
| VWF:FVIIIB | An assay that measures the ability of VWF to bind FVIII |
| FVIII | A clotting factor that acts as a cofactor in the formation of the Xase ['Tenase'] complex |
| FVIII:C | A functional assay of FVIII coagulant activity |
| FVIII:Ag | An immunological assay of FVIII |
| Ristocetin-induced Platelet Agglutination [RIPA] | A test that measures the ability of VWF to bind to and induce agglutination of platelets. Usually performed at several concentrations of Ristocetin. |
| VWF gene | The gene encoding von Willebrand Factor |
| F8 gene | The gene encoding FVIII |
The Classification of Von Willebrand Disease [VWD]
Von Willebrand Disease [VWD] is classified into Types 1 - 3.
| von Willebrand Disease [VWD] Type | Summary |
|---|---|
| Type 1 |
Partial quantitative deficiency of VWF Accounts for ~85% cases Autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance |
| Type 1C [Vicenza] | Increased clearance of VWF leading to Type 1 Phenotype Poor response to DDAVP Autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance |
| Type 2A | Qualitative deficiency of VWF Decreased VWF-dependent adhesion due to a loss of HMWM Autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance |
| Type 2B | Qualitative deficiency of VWF Increased affinity of VWF for platelet GpIb Autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance |
| Type 2M | Qualitative deficiency of VWF Decreased VWF-dependent adhesion but without a loss of HMWM Autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance |
| Type 2N | Qualitative deficiency of VWF Decreased binding of Factor VIII - may 'mimic' mild-moderate Haemophilia A Autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance |
| Type 3 | Virtual complete absence of VWF and Factor VIII Rare Autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance Patients with Type 3 VWD due to major gene deletions may form inhibitory antibodies following treatment |
| Platelet-Type vWD | Gain of function mutation in the platelet membrane platelet GpIb receptor Autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance |
HMWM - High Molecular Weight Multimers
1. The Diagnosis of Von Willebrand Disease [VWD] - Summary
The diagnosis of VWD requires a number of assays and an understanding of the principles of these assays.
| vWD Subtype | Assays ----- |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FVIII:C | VWF:Ag | VWF:RCo | VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio |
VWF:CB | VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio |
Multimers | VWFpp | Platelet Count | |
| Type 1 | N/↓ |
↓ | ↓ | Normal | ↓ | Normal | Normal Distribution | Normal | |
| Type 1C [Vicenza] | N/↓ | ↓ | ↓ | Normal or decreased | ↓ | Normal | Normal or increased HMWM | ↑↑VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio indicating increased clearance of VWF | Normal |
| Type 2A | N/↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | <0.6 - 0.7 | ↓↓ | <0.6 - 0.7 | Loss of HMWM | Normal | |
| Type 2B | N/↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | <0.6 - 0.7 | ↓↓ | <0.6 - 0.7 | Loss of HMWM | ↓ | |
| Platelet Type 2B | N/↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | <0.6 - 0.7 | ↓↓ | <0.6 - 0.7 | Loss of HMWM | ↓ | |
| Type 2M | N/↓ | ↓ | <0.6 - 0.7 | N/↓ | N/↓ | Normal | Normal | ||
| Type 2N | ↓↓ | N/↓ | N/↓ | Normal | N/↓ | N/↓ | Normal | Normal | |
| Type 3 | ↓↓ | Absent | Absent | - | Absent | - | Absent | Normal | |
In Type 2N VWD, the Factor VIII Binding [FVIIIB] assay is reduced.
2. The Diagnosis of Von Willebrand Disease [VWD]
Von Willebrand Disease [VWD] is classified into Types 1 - 3. The following investigations are important in making a diagnosis of VWD.
| Tests | Summary |
|---|---|
| Initial Investigations | |
| Clinical evaluation of bleeding symptoms | This can be difficult as mild bleeding problems are common in healthy individuals. The use of a standardised bleeding score can be very useful - see References and Bleeding Assessment Templates. |
| Family History | Establishing the presence of any significant family history suggestive of a bleeding disorder. |
| Initial laboratory tests | - Full blood count including platelet count - PT - APTT - Fibrinogen |
| First Level Tests: | |
| VWF:Ag | VWF:Ag is derived from an immunoassay that measures the total amount of VWF in plasma but provides no information on its function |
| VWF:Act | VWF:Activity refers to a functional assay of plasma VWF that uses a monoclonal antibody that targets the part of the VWF molecule that binds to the GpIb receptor. Other functional VWF assays may be undertaken and include: i. VWF Collagen binding assays [VWF:CB] ii. VWF Ristocetin-induced binding to the GpIbα receptor on platelets [VWF:RCo] iii. VWF Ristocetin-induced binding to a recombinant wild-type GpIbα fragment [VWF:GPIBR] iv. Spontaneous binding of a monoclonal antibody to a recombinant mutant gain-of-function GpIbα fragment [VWF:GPIBM] |
| VWF:RCo to VWF:Ag ratio | VWF:RCo assays measure the interaction between the A1 domain of VWF and GpIbα receptor to on the surface of the platelet. The VWF:RCo to VWF:Ag ratio can aid in the diagnosis of Types 2A, 2B and 2M VWD and helps differentiate them from Type 1 VWD. A VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio of <0.7 suggests the presence of a dysfunctional VWF i.e. a Type 2 disorder. |
| VWF:CB | VWF:CB assays measure the binding of VWF to Collagen. |
| VWF:CB to VWF:Ag ratio | A similar approach to the VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio, has been proposed for the VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio. In Type 2A VWD, the VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio is low. In Type 2B VWD, the VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio is low. In Type 2M VWD, the VWF:Ag concentration may be reduced or normal, but the VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio is usually normal. A VWF:CB/VWF:Ag ratio <0.7 may be seen with specific Type 2M variants that are associated with a specific collagen binding defect. |
| Factor VIII | Assaying FVIII is a first-level screening test in suspected VWD although FVIII levels may be normal in VWD. |
| Second Level Tests: Specialised laboratory tests |
|
| Factor VIII binding studies | These measure the binding of Factor VIII to VWF and can be of value in the identification of Type 2N VWD although this is not a widely available test and VWF gene analysis can be equally useful. |
| Multimer Analysis | VWF multimer analysis is a qualitative assay that analyses the variable concentrations of the different sized VWF multimers present in plasma. |
| Low Dose RIPA | Low dose Ristocetin-Induced Platelet Agglutination can be of value in identifying patients with Type 2B VWD. Low-dose RIPA will also be abnormal in patients with Platelet-Type VWD in which there is a gain of function mutation in the Gp1b gene. |
| VWF-propeptide assays | Measuring the VWF:pp and VWF:Ag ratio has been proposed as a means of identifying VWF variant proteins that are associated with a shortened half-life. |
| Additional investigations | |
| VWF:Ab | Binding of a monoclonal antibody [Ab] to the GpIbα binding site of vWF |
| VWFpp to VWF:Ag ratio | This is useful in studying patients with Type 1 VWD and in separating Type 1 patients with a normal VWF half-life from those with a shortened half-life e.g. Type 1C VWD [VWD Vicenza]. |
| VWF Inhibitor assays | Screening for VWF inhibitors by means of a conventional inhibition assay [a mix of normal and test plasma and then assaying VWF levels] is very difficult . A standard Bethesda-type inhibitor assay will frequently fail to identify a VWF inhibitor. ELISA assays have been published for looking for VWF inhibitors but again do not always identify antibodies. The history can be very important in such cases as there is frequently no history suggestive of a bleeding disorder until very recently. The half-life of infused VWF is also decreased and establishing this can be very useful. The measurement of the VWFpp/VWF:Ag ratio can also be very useful. |
| VWF:FVIIIB | The FVIII Binding Assay [VWF:FVIIIB] measures the amount of FVIII that can be bound by VWF. In a case of Type 2N VWD this capacity is reduced. If the VWF:FVIIIB/VWF:Ag ratio is <0.7 this is consistent with Type 2N VWD. The VWF:FVIIIB assay is not a widely performed assay and in some labs, it has been replaced by VWF and F8 mutational analysis. |
| VWF Mutational analysis | Sequence analysis of the VWF gene is relatively simple to perform but is complicated by the presence of a partial VWF pseudogene [exons 23-34] on chromosome 22. |
Click HERE to access a PDF that summarises this information in more detail.
The algorithm below outlines a possible approach to the investigation of a patient with suspected VWD.
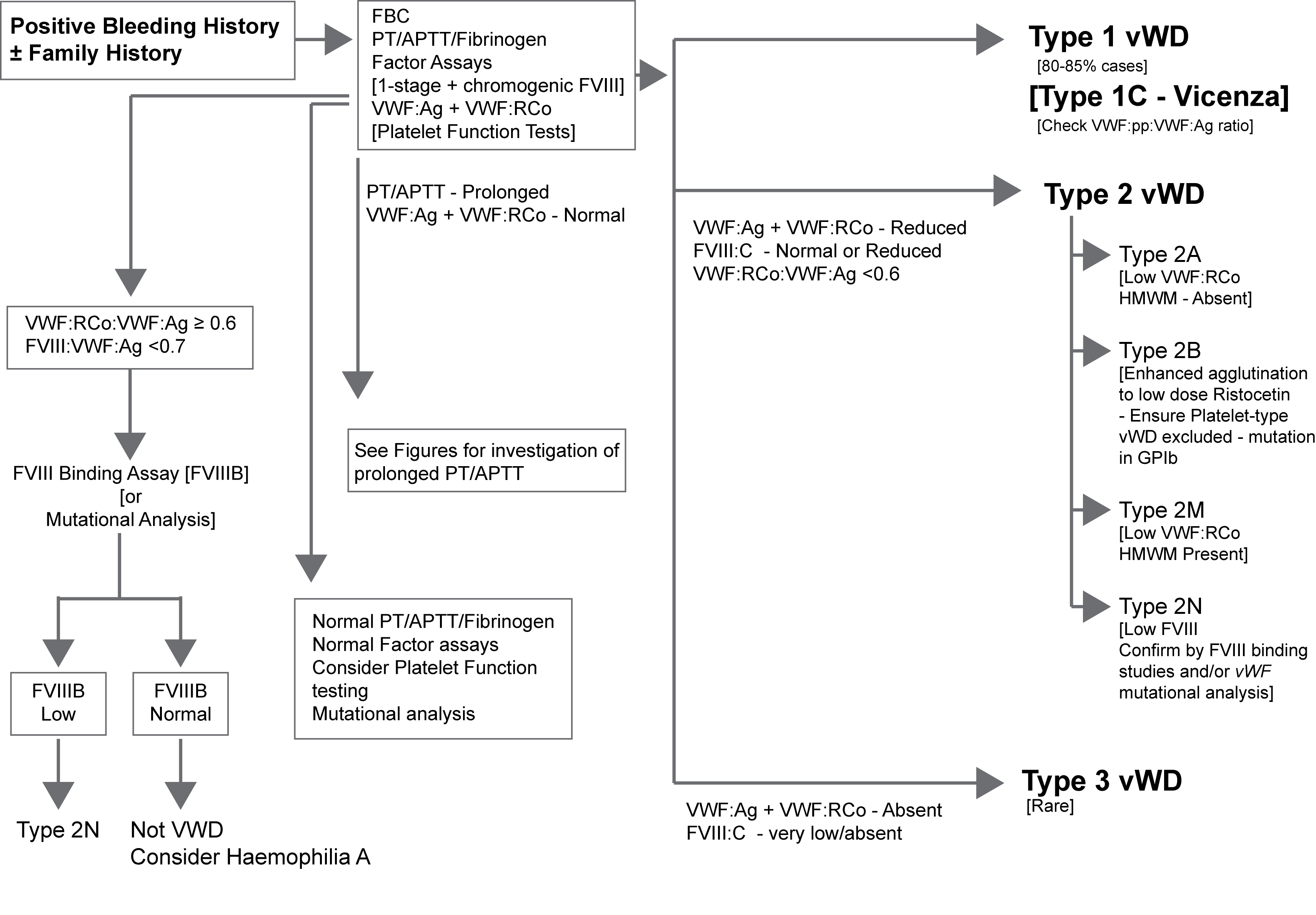
The various assays outlined in the flowchart are discussed in more detail under VWF Assays.
Click HERE to return to the top of the page.
